MBR Partition Scheme
MBR partition table scheme
saves partition information on the first sector of disk. The entry for each
partition is 16 bytes and the total is 64bytes, thus the maximum entries MBR
partition table can save is four. That is to say MBR partitioning can have up
to 4 partitions. But many users are not satisfied with 4 partitions and want to
create more partitions. To eliminate this limitation, extended partition is
introduced. Users can create multiples logical partitions in an extended
partition. The following picture shows MBR partition scheme.
GPT Partition Scheme
Compared with MBR, GPT is
relatively new partitioning scheme. If your computer is brand new and it is
likely to use GPT partitioning scheme. GPT is much more complicated and this
part will dig a little about it. If you are not into technical details you can
skip this part to read its main features.
First, you may notice that this picture uses LBA 0, LBA 1…to
represent disk address, which used CHS (Cylinder-Head-Sector) addressing
method. LBA (Logical Block Addressing) method is another important method to
partition mass storage device such as hard drives and SSDs. LAB 0 means the
first sector whose physical number is 0 and LBA represents the second sector
whose physical serial number is 1.
How to choose partition plans between MBR & GPT?
This post talks about MBR and GPT partition able and the previous
section explains basic information about BIOS and EFI. This part devotes to how
to choose partitioning scheme.
BIOS + MBR
If motherboard in your computer is BIOS or UEFI with BIOS mode,
MBR partition plan is the correct choice.
UEFI + GPT
Oppositely, if your computer is using UEFI motherboard and enables
UEFI mode, then please employ GPT partition scheme.
You might be confused by the conclusion above, as there are many
guides online teaching users to install operating system on BIOS+ GPT or UEFI
+MBR. My advice is that if you are not technical geek or professional user, you’d
better choose BIOS + MBR or UEFI +GPT, as you can benefit:
1. Better performance in hardware and software, faster speed.
2. Avoid many potential issues that may occur to installation or
running Windows. Professional users can easily fix these problems, but common
users can’t get rid of any system errors easily.
Some users may ask whether it is OK to use Legacy BIOS if the
motherboard is UEFI. The advice is that for the consideration of performance
and speed do not use Legacy BIOS unless hard drive’s capacity is very small. EFI+GPT
takes more disk space (100MB or so) than BIOS+MBR, if 100MB matters much on
your hard drive, you can choose Legacy BIOS.
How to convert MBR to GPT without data loss?
Step 1: Launch
PartitionGuru from your computer. Select hard drive you want to convert and
click “Disk” to select “Convert to GUID Partition Table”.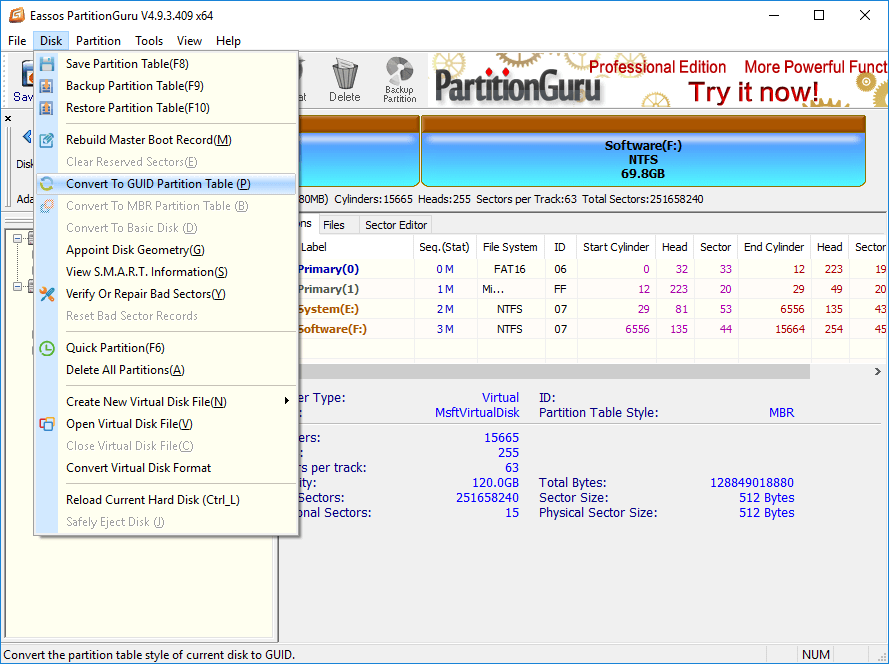

Step 2: Click “Yes” on the
message box. Please note that only new operating system can use GPT disk, for
example, 32-bit Windows XP does not support GPT disk. Also, only the EFI-based
computer can boot from GPT disk. Thus your computer won’t be able to boot
normally if it doesn’t support GPT and you need to reinstall Windows.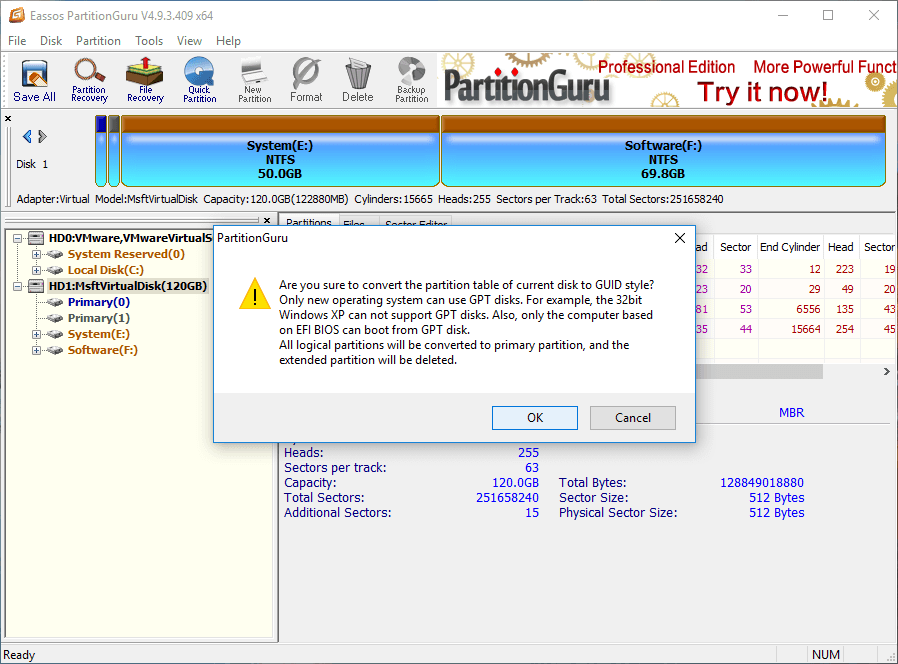

Step 3: Click “Save All”
button and the conversion takes effect.
Article source: http://www.eassos.com/tutorial/hard-drive/mbr-vs-gpt.php